Our video and audio calling functionality is implemented via WebRTC, which is a peer-to-peer communication library, open-source, supported by Google, Apple, and Microsoft, among others. The react-native-webrtc library made it possible for WebRTC protocol to be integrated into our React Native projects. It works for both iOS and Android, and video calls are even possible from an iOS device to an Android device and vice-versa.
Data Flow Overview
- When a user initiates a call, we send that down to Firebase (which is used as the signaling server)
- The other users’ devices are observing the Firebase signal and when they retrieve it, they pop up the incoming call screen
- When another user answers the call, we signal the operation to Firebase again, which now sends the new signal back to the initial caller and the video / audio call starts
- We use Google’s and Mozilla’s STUN and TURN server for the actual peer-to-peer communication
const servers = { iceServers: [ { urls: 'stun:stun.services.mozilla.com' }, { urls: 'stun:stun.l.google.com:19302' }, { urls: 'turn:numb.viagenie.ca', credential: 'beaver', username: '[email protected]', }, ], };If you have your own server, you can update these URLs, or you can simply just continue using these.
Codebase
All the code related to audio video calls lives in src/Core/chat/audioVideo. Among the most important classes, we can list:
- IMAudioVideoChat
- This is the core component managing the calls, such as initiating a call, accepting a call or hanging up
- It interacts directly with the WebRTC library
- Renders the incoming / outgoing calls screen for both audio and video calls
- AudioChatView
- This is the React component in charge with the audio calling UI once the audio call started
- Its only function is to render the UI
- VideoChatView
- This is the React component in charge with the video calling UI once the video call started
- Its only function is to render the UI
- firebase.js
- This is the class containing all the methods that are necessary to make Firebase our signaling server
- This is the file that you need to modify if you want to use a different backend
- It is in charge of
- observing incoming signals
- sending new call signals
- accepting new incoming streams (such as for each new participant into a group chat)
- audioVideoChat reducer
- lives in redux/index.js
- this is the reducer allowing your React Native screens to listen to incoming calls (the signals)
- you must add this reducer to your app if you need to integrate our video chat into an existing app
Enable Push Kit & Call Kit with Apple’s APNs
Push Kit enables your app (on iOS) to retrieve incoming calls when the app is in background, forced quit, or in locked screen. Call Kit enables your app to display the native incoming call screen UI (on iOS). This is particularly important when your iOS app is not in foreground (so in background or locked screen), since it allows the call recipient to accept an incoming call. To enable Push Kit in your app, you’ll need a server that makes the call requests to Apple’s Push Kit APNs. Fortunately, we’ve included this server code in the archive you’ve purchased. It comes as a Firebase function – check out the Firebase folder. To enable Push Kit & Call Kit, simply follow the steps:
- Generate a .pem certificate with your Apple Developer account and the Bundle ID of your app. Find any online tutorial in case you didn’t do this before.
- Override voipCert.pem file with your own certificate.
- In Firebase/functions/pushKit.js, change two lines of code to update the correct password and the correct Bundle ID (of the iOS app):
const config = { production: false, /* change this when in production */ cert: 'voipCert.pem', key: 'voipCert.pem', passphrase: 'INSERT YOUR PASSWORD HERE' };notification.topic ='io.instamobile.chat.swift.voip'; // change this to your own Bundle ID. You have to add the .voip suffix here!!!
- Enable Billing for your Firebase project (see official docs on how to enable billing) – don’t worry, Google won’t charge you until you reach a certain traffic/userbase (see Firebase Pricing)
- Deploy the Firebase function to your own Firebase, by running
firebase deploy
in the Firebase folder.
- Update Push Kit Configuration in React Native In Core/chat/config.js, update the Push Kit Endpoint and the Bundle iOS ID with your own (the Push Kit Endpoint will be retrieved after you ran “firebase deploy” at step 4). The Bundle ID is the app identifier you chose initially when you created the iOS app in Firebase Console.
const callID = 'E621E1F8-C36C-495A-93FC-0C247A3E6E5F'; const pushKitEndpoint = 'https://us-central1-production-a9404.cloudfunctions.net/initiateChatCall'; const iOSBundleID = 'io.instamobile.chat.rn.ios'; export { callID, pushKitEndpoint, iOSBundleID };
Now you will notice your function deployed properly in Firebase Console -> Functions. You can view the logs every time this method is called. 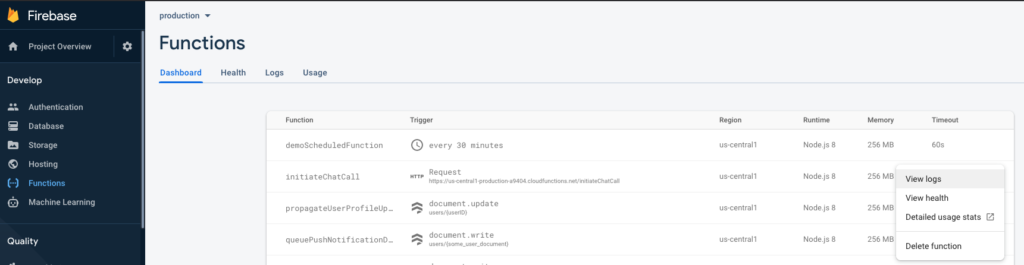 Go ahead and initiate a call between two users – you’ll notice this function will get called, and the recipient user will get a VoIP push notification call. Debugging If you don’t see any logs in Firebase, for the initiateChatCall function, this means the user that you call does not have a pushKitToken. This can happen for multiple reasons, such as they never opened the app, or they rejected the push notification permission dialog. To check whether the user has a push kit token, simply find that user in the “users” Firestore table, and see if their pushKitToken field is set up. If you do see logs in Firebase – Successful logs look like this
Go ahead and initiate a call between two users – you’ll notice this function will get called, and the recipient user will get a VoIP push notification call. Debugging If you don’t see any logs in Firebase, for the initiateChatCall function, this means the user that you call does not have a pushKitToken. This can happen for multiple reasons, such as they never opened the app, or they rejected the push notification permission dialog. To check whether the user has a push kit token, simply find that user in the “users” Firestore table, and see if their pushKitToken field is set up. If you do see logs in Firebase – Successful logs look like this
{"sent":[{"device":"dae0721aef5713027f7efdbf2da5d3dec3cc0df3830facd2cccf1ef96122efa8"}],"failed":[]}
Since the “failed” field is empty, it means the request has been properly set up (correct certificate, correct bundle ID, correct password) so everything should work. Sometimes Apple APNs are a little flaky, especially when not in production, so be patient or try to initiate a call again. Failed logs look like this:
{"sent":[],"failed":[{"device":"grgwrehe69eafe441a12e34a505620","error":{}}]}
In this case, you did not set the correct Bundle ID, the correct .pem certificate or the correct password. You’ll need to go over steps 1-4 again and figure out what you missed.
Background & Locked Screen Calls on Android
To enable calls on Android while the app is in background or the device is locked, React Native uses ConnectionService (via the react-native-callkeep library). To support signal the calls between devices, remote notifications are being used, via Firebase Cloud Messaging. To enable these type of calls, you must first ensure that push notifications are working fine in your environment (e.g. push notifications when sending a text message). To be able to receive calls in background / on locked device, when in debug mode (so when the app is built from the command line), you must make sure that when the app opens, you accept the “Phone Accounts” permissions. This is done in a separate Settings screen that can be opened by clicking the dialog below (left screen). Make sure that your app’s permissions is on (the right screen), then tap the back button on that screen to go back to the app. When closing the app, check that the right screen option for your app is still ON.  In the production environment, you won’t need to do this, since the users accept that permission when downloading the app from the Play Store.
In the production environment, you won’t need to do this, since the users accept that permission when downloading the app from the Play Store.
Integrating Video Chat into an Existing React Native App
If you already have a React Native app, and you’d like to integrate our video chat feature, we made it extremely easy for you to do so. Here’s an overview with the steps you need to follow:
- Import src/Core/chat/audioVideo folder into your src folder
- Add the audioVideoChat reducer to the lists of your supported reducers
- In one of your main components (e.g. HomeScreen), connect to that reducer
const audioVideoChatConfig = useSelector(state => state.audioVideoChat);
- When rendering your main UI, simply render video chat functionality too based on the reducer:
{audioVideoChatConfig && <IMAudioVideoChat {...audioVideoChatConfig} />}
Configuring Twilio
To use Twilio service for audio/video call, you need to navigate to src/Core/chat/audioVideo/index.js file and change this line:
export * from './webRTC'; // export * from './twilio';
to:
// export * from './webRTC'; export * from './twilio';
Next, find src/Core/chat/audioVideo/twilioServerMiddleware folder. At the root of this folder, deploy a firebase cloud function. But before that, you will need to:
- Run
npm install -g firebase-toolsto install firebase CL. - Run
firebase loginto log in via the browser and authenticate the firebase tool.
After successfully running the commands above, run:firebase deploy --only functions to deploy your function. If you encounter any error, visit the official documentation here for assistance. Now, navigate to src/Core/chat/audioVideo/config.js file and edit:
export const TWILIO_SERVER_ENDPOINT = 'https://us-central1-socialape-e8afb.cloudfunctions.net/getTwilioAccessToken';
In the code above, change “socialape-e8afb” to your firebase Project ID. You need to do only the steps above for ios. For android, you need some extra steps before Twilio works. You will need to navigate to react-native.config.js at the project root and replace this line of code:
dependencies: {
'react-native-twilio-video-webrtc': {
platforms: {
android: null, // enable/disable react-native-twilio-video-webrtc on Android platform.
},
},
'react-native-webrtc': {
platforms: {
// android: null, // enable/disable react-native-webrtc on Android platform.
},
},
},
to:
dependencies: {
'react-native-twilio-video-webrtc': {
platforms: {
// android: null, // enable/disable react-native-twilio-video-webrtc on Android platform.
},
},
'react-native-webrtc': {
platforms: {
android: null, // enable/disable react-native-webrtc on Android platform.
},
},
},
Also, you should delete the build folder that exists at android/app/build. Rebuild your android project from the command line to have the changes take effect.